Stuff:
• Thin sheet of cardboard,
• Any petroleum jelly like,
• Vaseline gel,
• Glitter dust/ sand/ chalk powder,
• String, Rubber ball,
• Scale,
• Pencil,
• Scissors
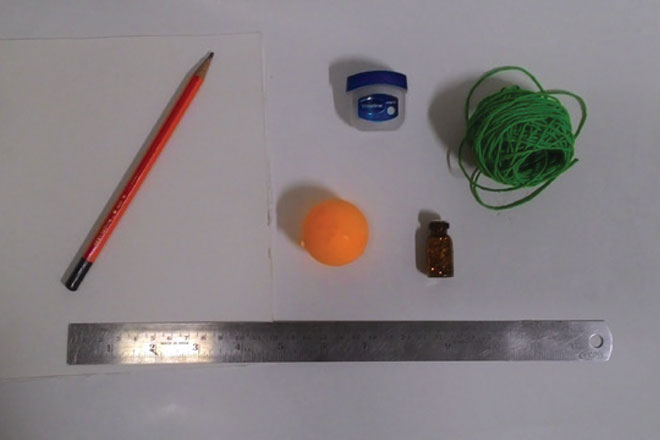

Do:
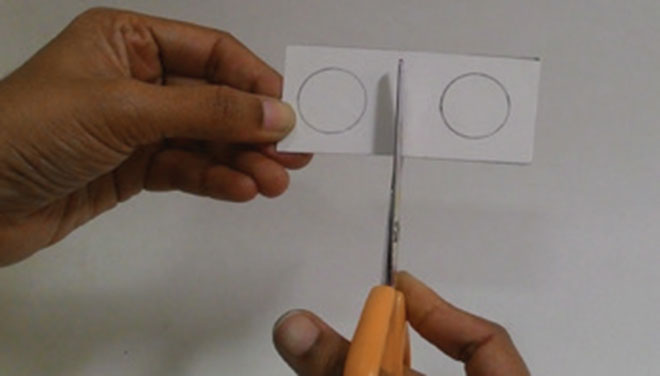
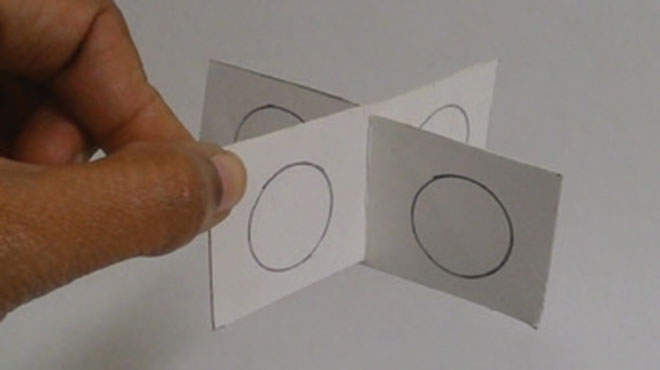
1. From the cardboard, cut 6 rectangles of equal size (3 x 1.5 inches). Draw two circles on each rectangle as shown.

2. Using scissors, make a slit in the centre of each rectangular sheet.
3. Fix two sheets at the slit as shown to form your satellite. Make two more. Smear petroleum jelly on the circles.
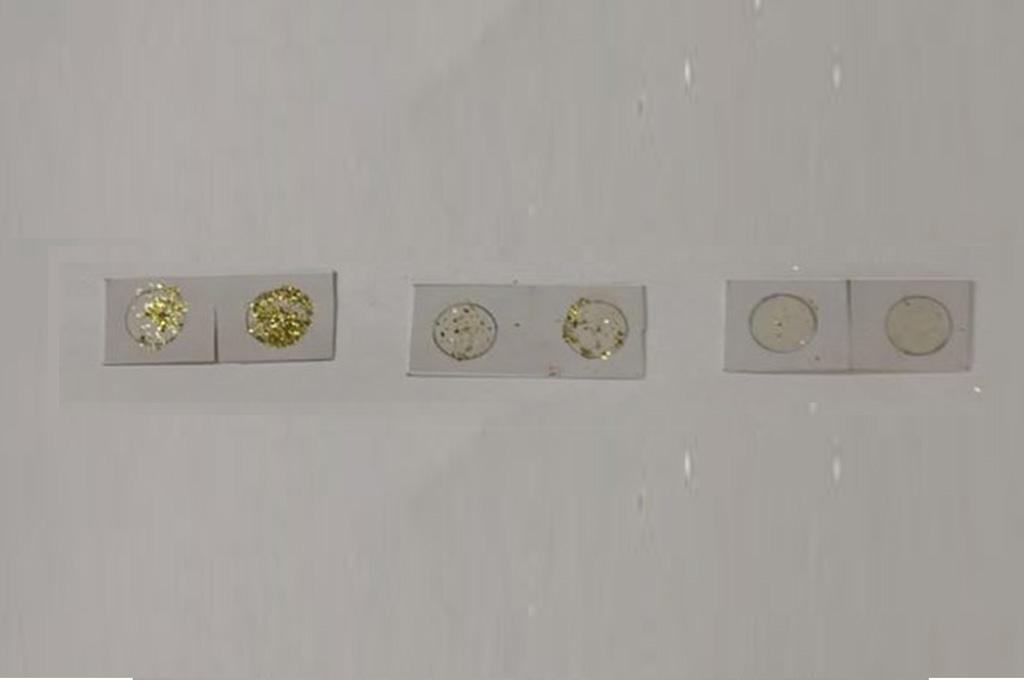
4. Take three pieces of string of different lengths—5, 10 and 15 inches. Attach one end of the string to a satellite and the other to the scale as shown. Suspend the satellites over a pile of glitter dust or fine sand and throw the ball into the pile.
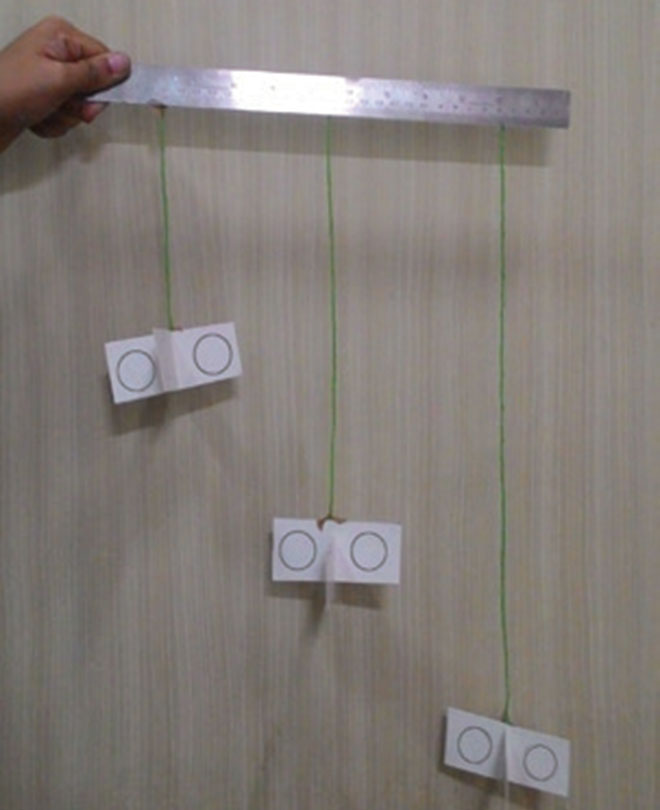
See
When you throw the ball into the pile of glitter or sand, it sends up a cloud of dust which is collected by your satellites, the amount varying according to their distance from the pile.

Think About
How do our “satellites” collect dust?
The cardboard cutouts and the strings attached to the scale simulate the satellites and their orbits. Their distance from the pile of glitter dust represents their different orbits around the comet. The impact of the ball on the glitter dust represents the dust cloud that results from a meteor impact. When we throw a ball on the pile of glitter dust, it scatters and the glitter particles are stuck to the “satellites” because of the petroleum jelly smeared on their surface. Besides studying the dust, scientists would also be able to calculate the distance of the satellite to the comet by analysing the amount of dust collected and the distance between the particles as would be evident in our cardboard satellites.
Let’s Find Out
How does an actual satellite collect stardust?
NASA launched the StarDust Mission satellite in 1999 to fly along the orbit of the comet Wild 2, and collect dust from it. The satellite was designed with a special collector plates filled with a special type of gel called aerogel that could trap the particles as they came in contact with it. When the satellite returned the stardust samples to Earth 7 years later in 2006, the trace of each particle could be seen in the aerogel. Each single particle was cut out of the gel and examined. One of the finds revealed the presence of amino acid glycine, one of the building blocks of life.